Mobile apps are a huge part of our daily lives. The demand for mobile apps just keeps on growing, as does the need for an efficient mobile app development process.
The procedure of developing an app can be pretty complex and challenging. It covers everything from product discovery to UI/UX design, active development, testing, deployment, and post-release maintenance.
This article will give you a better understanding of the complete pathway of mobile app development. We'll break it down into the main steps that we've developed at Codica to build successful mobile apps.
So, let's take a look at different stages of mobile app development and see how they will help you make your app a viable product.
4 main types of mobile apps
Before you get started on any mobile app development processes, it's a good idea to decide on the app type first. Why is that? The way you develop the app can vary a lot depending on which approach you choose.
To make sure your app development process goes well, it's important to follow a clear plan that uses the best ways to do things and follows industry standards.
In this section, we'll take a look at different app types that have their own specifics in terms of development. You can choose between them depending on your business goals.
1. Native app
A native app is designed to run on a specific operating system, making it platform-specific. This means that in order to launch an app on both iOS and Android, businesses must develop separate apps coded specifically for each platform.
Although building a native application can be costly, it often results in better performance and an improved user experience. Spotify is a great example. It’s a native music app optimized for both iOS and Android operating systems.
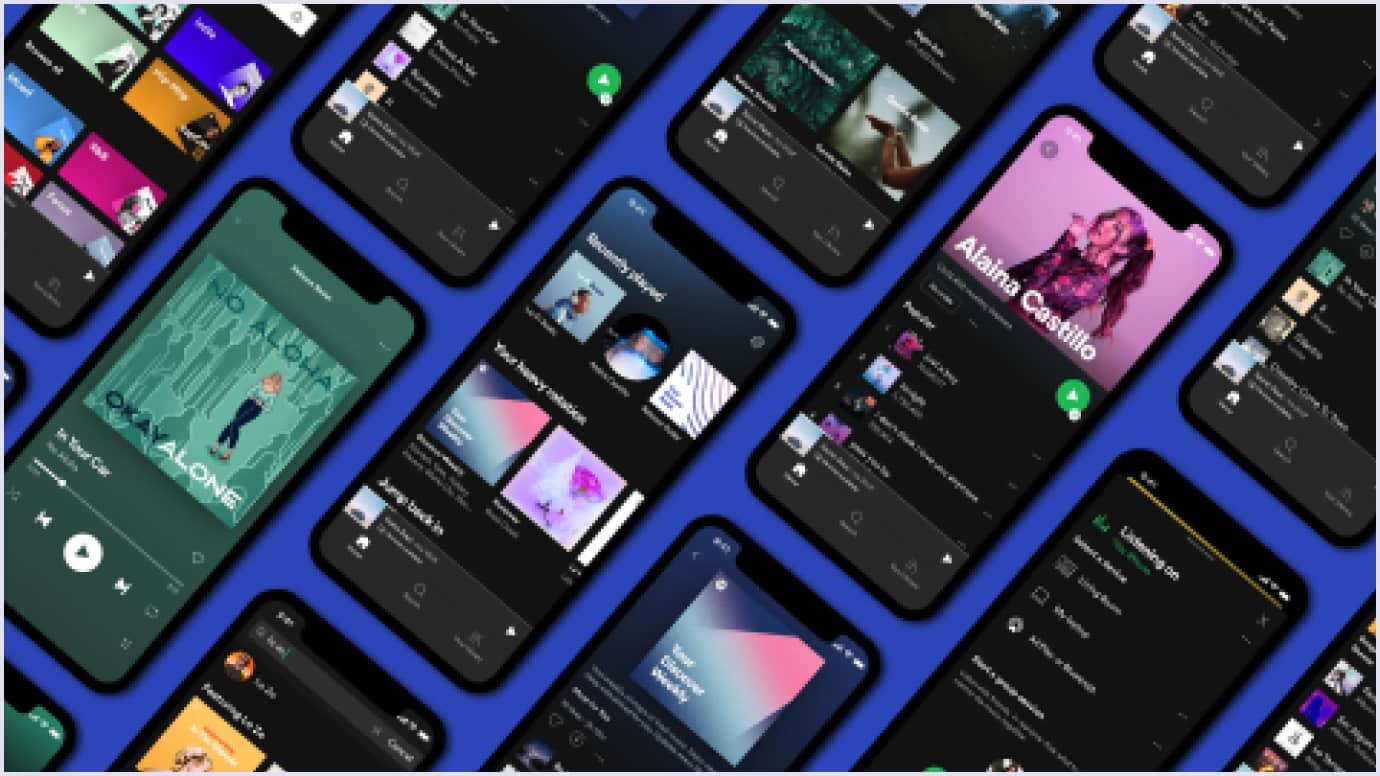
Source: Spotify
2. Cross-platform application
Cross-platform applications are designed to run on multiple operating systems (iOS, Android, etc.) using a single codebase.
Popular frameworks like Flutter, React Native, or Xamarin allow developers to write code once and deploy it across platforms, reducing development time and costs.
While cross-platform apps may not match the performance or native feel of fully native apps, they provide a good balance between efficiency and user experience. Well-suited for businesses seeking a cost-effective way to reach a broader audience, these apps are ideal for simpler use cases.
Source: Trend Hunter
3. Hybrid app
A hybrid app is a combination of a native mobile app and a web app. Essentially, a hybrid app is a web application that's placed into a native shell. When downloaded, the app appears and functions similarly to a web app, but it's built using a native container.
Hybrid apps are always more efficient to build. They are simply faster and more straightforward development-wise. However, they may be prone to performance issues. For instance, Evernote is a world-known hybrid app that's available on multiple platforms, including iOS, Android, and desktop devices.
Source: Tigren
It allows users to create and store notes, documents, and other content in a hybrid environment that combines native and web technologies.
4. Progressive web application
A progressive web app (PWA) is a type of web application that provides users with a native app-like experience. Unlike traditional native apps, PWAs run on the web, which means that users don't need to install a separate app to use them.
One of the significant advantages of PWAs is that they consume less data and perform better than traditional web apps. They also tend to increase user engagement rates, making them a popular choice for businesses and developers looking to create high-performance web applications. Let’s take Impact as an example.
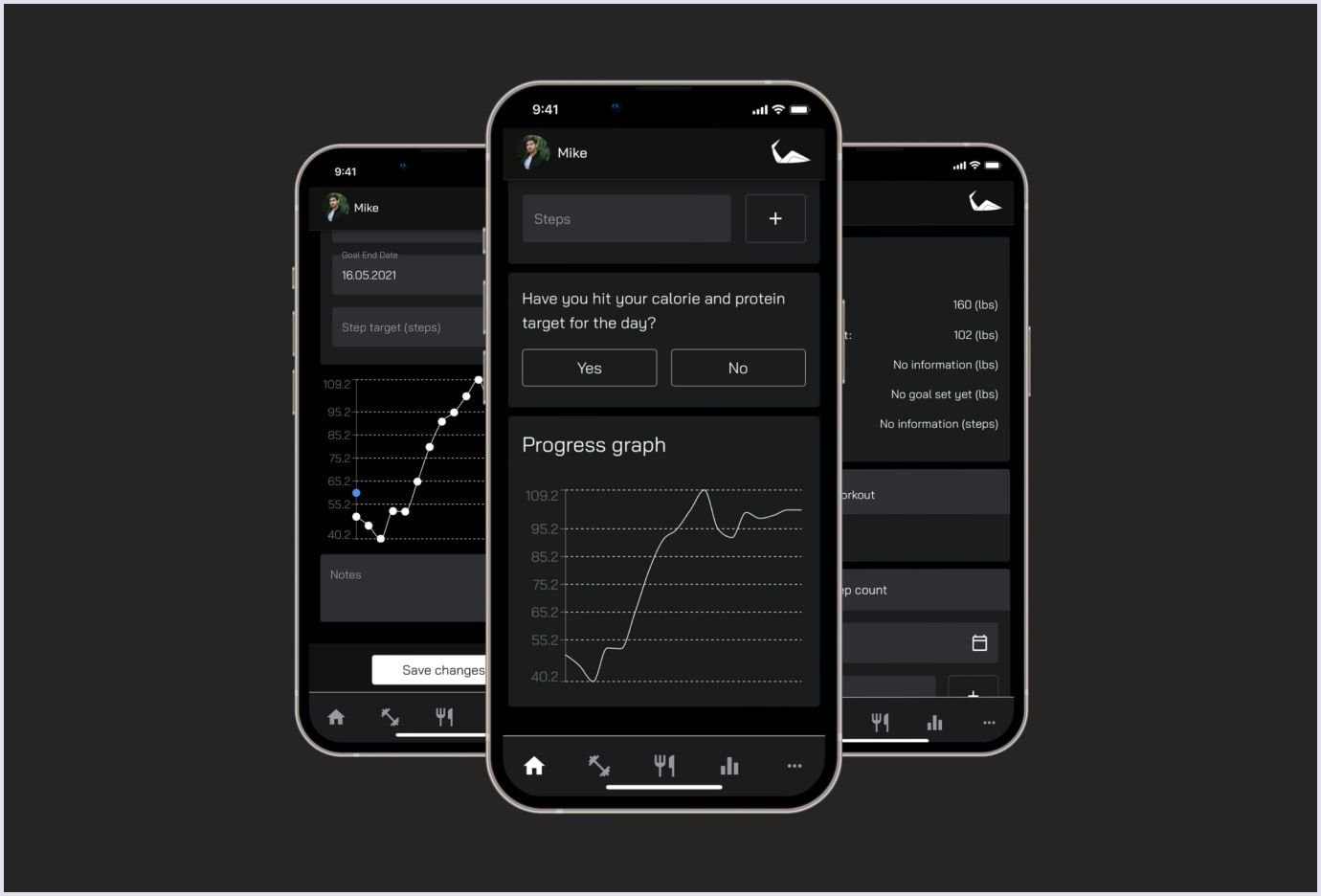
Impact Personal Training is a progressive web app the Codica team has built from scratch. It is a complex fitness app created to help people simplify their training. Thanks to the cross-platform nature, this PWA solution allows users to quickly access their training sessions, track their performance in charts, and create nutrition programs on their smartphones and desktops. Here’s a short showcase of how it works:
The lowdown on how we develop mobile apps: 7 main steps
Step 1: Product discovery
This is the most crucial point in the whole strategy development timeline. Notably, there are various names for this stage, including the product discovery process that we conduct at Codica.
At the core of this process lies the foundation of your app, its idea, and its philosophy. Apart from them, there are more practical ones. For instance, we help our clients to identify objectives throughout the development journey. We select the right platform to cover more users, choose monetization means, and research potential rivals in the market. Throughout the years we conducted it, we learned best about those crucial aspects.

Let’s list them in more detail now.
Identify objectives
It is essential to identify objectives during the strategy planning phase in mobile app development. They can provide direction and focus for the entire app development process. In short, objectives can be defined as measurable and understandable goals. They usually align with certain results that you hope to accomplish.
Clarifying objectives can assist in guaranteeing many things. For example, the team responsible for developing the app is in agreement and working together to achieve a shared objective. You can find it really helpful in allocating resources or prioritizing certain development tasks. Hence, it will allow you to make moderate decisions throughout the process.
Choose your platform
When choosing a platform for your mobile app, consider three options: Android, iOS, or cross-platform.
Start by researching your audience and their preferred platform. If most users favor iPhones, focusing on iOS makes sense.
Next, factor in your budget and resources. Developing for both platforms can be costly, so you might start with one and expand later. Ensure your desired features are supported on the chosen platform.
Lastly, be mindful of platform guidelines. For example, Apple’s App Store has stricter rules, which can affect the deployment process. We'll cover this in detail later.
| Aspect | Android | iOS | Cross-platform |
| Language(s) | Java, Kotlin | Swift | React, JavaScript, TypeScript, Flutter, Ionic |
| Development environment | Android Studio | Xcode | Varies by framework |
| Distribution store | Google Play Market | Apple App Store | Both |
| Market share | 70% globally, especially strong in regions like India, Brazil, and Indonesia | 27% globally, dominant in the US, Canada, and Western Europe | Smaller share compared to native platforms but growing steadily |
| Development time | Longer development time due to device fragmentation and compatibility issues | Shorter development time due to consistency in devices and software | Significantly shorter development time, but may require time to conform app to both platforms |
| User demographics | Popular among basic to highly advanced tech users and regions where cost-effective solutions are important | Popular with high-income and urban users and affluent areas | Suitable for a wide range of users |
| Monetization | Ad-supported, in-app purchases, paid apps | In-app purchases, paid apps, subscriptions | Similar monetization options as Android, but may generate more revenue due to wider operation |
| Submission process | A relatively lenient approval process | Strict approval process and high standards | Varies by platform and store |
| Updates | Frequent OS updates but slower adoption rates | Frequent OS updates and very fast adoption rates | Varies by platform and requires more time to import new technologies |
| User experience | More customizable and flexible UI/UX options | Consistent and intuitive UI/UX design | Varies depending on the framework and development approach |
In conclusion, Android and iOS are the two dominant platforms, each with its own unique advantages and disadvantages.
Android is more popular than iOS worldwide, especially in emerging markets. However, the wide variety of devices and screen sizes can make development more time-consuming. iOS, on the other hand, is popular among users in affluent regions who prioritize premium devices. It offers a simple design, requires less time for development, but the app approval process can be more stringent.
Ultimately, the choice between these platforms will depend on your specific needs and goals, as well as those of your target audience and your budget.
Choose monetization method
Choosing a monetization model is crucial for any app because it determines how you will generate revenue from your product. Without a clear monetization strategy, it can be challenging to sustain the development and operation of your app in the long run.
Here are some reasons why choosing a monetization model is important:
- Revenue generation. A proper monetization model helps you generate revenue from your app. You need to decide how you will make money from your app to cover your development and operational costs and make a profit.
- User expectations. You can set clear expectations for your users by choosing a monetization model. They always want to know what they're paying for or if they're paying at all. By providing clarity, you can improve user trust and retention.
- Market competition. The app market is very fierce, and choosing the right monetization model can give you a competitive advantage. By offering a unique and appealing pricing strategy, you can attract more users to your app and stand out from your competitors.
- Scalability. A monetization model can help you plan for the future and scale your app. You can adjust your pricing strategy as your user base grows or as you introduce new features.
- Investor interest. Investors may be more interested in your app if you have a clear monetization model. They care about how much revenue your app will generate and how it will perform in the long term.
Let’s list the most common mobile app monetization models referring to another article of ours. Once again, clarity is crucial in such a complex topic. Mobile app monetization is a crucial aspect of app development. It directly affects the app's revenue and sustainability. The three most popular monetization models include subscription-based, in-app purchases (IAPs), and in-app advertising (IAA). Each model has its pros and cons, and the choice of the best model for an app depends on many aspects.
| Model | Definition | Pros | Cons |
| Subscription-based model | Users pay a monthly/yearly recurring fee to access the app's features, content, or additional functionality. |
|
|
| IAPs (in-app purchases) model | Users pay to unlock additional features or content within the app. |
|
|
| IAA (in-app ads) model | Allows the app to display ads from third-party advertisers; Generates revenue from the ads shared between the app and the advertiser. |
|
|
A successful monetization model should ultimately balance user experience (UX) and revenue generation to create a sustainable business model.
Analyze the market and research competitors
In such a competitive market, it can be challenging to create an app that outstands and outperforms others. The competitor analysis and market research can be helpful in this matter. Let’s figure out why it is important in the first place.
- Helps identify user needs. Researching competitors helps you find out what is already out there and what you can add for customers in your mobile app. This helps you create an app that users want and that is different from competitors.
- Provides an understanding of the market trends. Researching the market helps you know new mobile app development trends. This helps you create an app that users want to use and beats outdated apps.
- Makes room to create a unique value proposition. Understanding your target audience, competitors, and the market helps you create an outstanding value proposition for your app that sets it apart from others. This can help you attract users and build a loyal user base.
- Allows to mitigate risks. Target audience, market, and competitor research can identify potential risks and challenges that your app may face. By understanding these risks, you can prepare for them and mitigate them as much as possible.
Step 2: Analysis and planning
Given the idea that the product discovery phase is extremely vast and covers many aspects, it would be more convenient to divide its overview into two parts. Apart from the strategy planning we discussed, we also dedicate time to collecting and documenting requirements. As a result, our clients receive a detailed technical proposal for software development. However, there are several more checkpoints.
Functional and non-functional requirements
- Functional requirements imply and are the foundation of your app. They stand for the specific features and capabilities that your app must have to meet the minimum users' expectations. These can include things like data management, authentication, and many other features that protect users.
- Non-functional requirements (i.e., non-behavioral), on the other hand, are the technical and performance characteristics that the app must exhibit in order to be considered functional. Usually, they include: accessibility, performance, usability, portability, and security.
Once again, let’s summarize everything in a table.
| Criteria | Functional requirements | Non-functional requirements |
| Purpose | Define the core functionality the app should have, its features, and its behavior. | Define the app’s performance and what quality of service it should offer. |
| Importance | Essential to the app's success, as users expect it to work as intended/advertised. | Equally important as functional requirements, as they determine the app's overall quality and user satisfaction. |
| Priority | Prioritized based on their importance to the app's core features. | Prioritized based on their impact on the user experience, such as response time, availability, and reliability. |
| Measurability | Can be tested through manual or automated testing. | Measured through performance testing, load testing, security testing, etc. |
| Changeability | They are typically fixed, as they are determined by the app's architecture, infrastructure, and technical constraints. | This may change as user needs evolve or new features are added. |
| Examples | User authentication, navigation, data input/output, notifications, etc. | Response time, network connectivity, battery usage, storage capacity, accessibility, etc. |
Defining both functional and non-functional requirements is helpful. They help to ensure that the app meets users’ needs and is technically sound and reliable. This involves identifying the specific features and capabilities that are necessary for the app to function as intended. They also assess the technical and performance characteristics that are necessary for the app to be successful in the long run.
Product roadmap
The roadmap stands for a strategic document. It outlines the direction, goals, and priorities of a mobile app's development over a specific period. It provides a high-level overview of the app's planned features, functionalities, and improvements. The roadmap also defines the timeline for their release. Here’s what a product roadmap normally looks like.
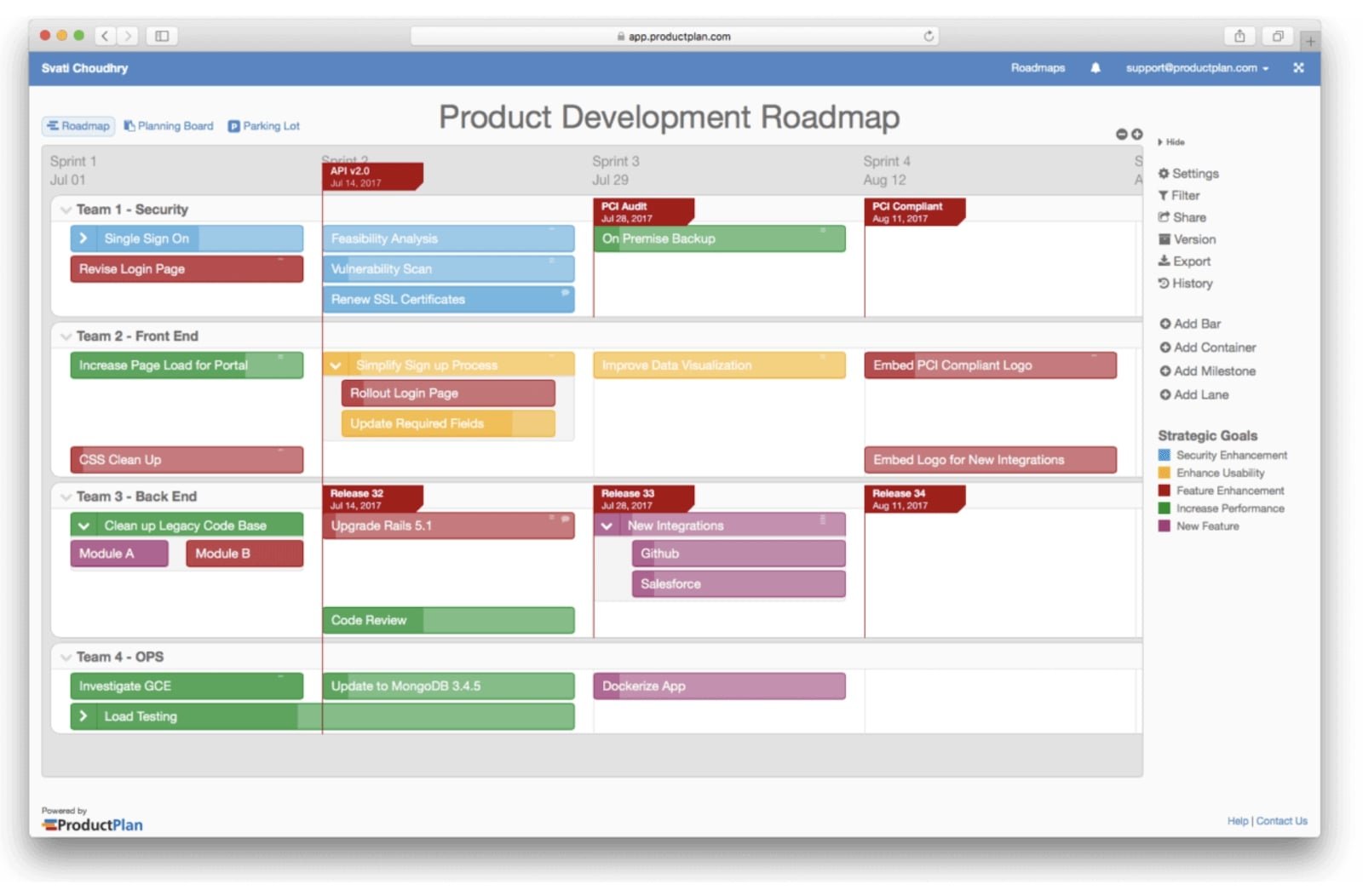
Source: ProductPlan
A proper product roadmap can include client feature requests, internal input, and customer app ideas. Normally, the contents of a roadmap are always coordinated with the product strategy.
Let’s list several key features a typical roadmap in mobile app development has to consist of.
- Objectives. They stand for measurable, specific, and time-bound targets with clearly defined success metrics. Objectives are critical milestones that must be achieved to deliver your product successfully.
- Themes. These are high-level categories of work that describe how your efforts will support your objectives. Themes show how specific releases and features contribute to your overall strategy.
- Product releases. They represent the launch of new product functionalities depicted on a timeline. A release typically includes multiple features that are delivered simultaneously.
- Epics. These are larger bodies of work that often span multiple releases, similar to categories. Teams usually divide epics into smaller milestones and deliver them incrementally over time.
- Features. They represent specific pieces of new or improved functionality. They are usually related to your app's components, appearance, capabilities, and performance.
- Timeline. This is a schematic representation of product release dates over a certain time period. For instance, the timeline's scale can be set to days, years, or quarters. This variable depends on how detailed the project is and its required dedicated hours.
Technology stack
Selecting the appropriate mobile app tech stack is a vital decision. It can substantially influence the triumph of your application. The technology stack consists of frameworks, programming languages, libraries, and tools for developing your app.
Here are two factors you should care about before choosing:
Platform
Your tech stack depends on the platform you're developing for: iOS, Android, or both. To build an iOS app, you need to use Swift. Apple regularly updates it to meet modern users' standards.
To build an Android app, you can use Java or Kotlin. Both have pros and cons, but they're still the market leaders thanks to their flexibility. For cross-platform development, the most popular frameworks are React Native or Flutter. React Native is more comprehensive with a big community, while Flutter is still new.
Functionality and complexity
There is no best technology stack. You have to choose based on different things. If your app needs real-time updates, you may need a database like Firebase. If your app needs lots of processing, you may need to use a language like C++ or Rust.
For apps with complex UI/UX design, use a framework like React Native or Flutter, which offers lots of pre-built UI components.
Step 3: UI/UX design
User interface (UI) and user experience (UX) are crucial components in successful mobile app development.
In the UI/UX design services we provide, UI represents the layout and design of the app's interface. UX, in turn, represents the overall user experience. It includes ease of use, navigation, and the overall feeling the user has when using the app.
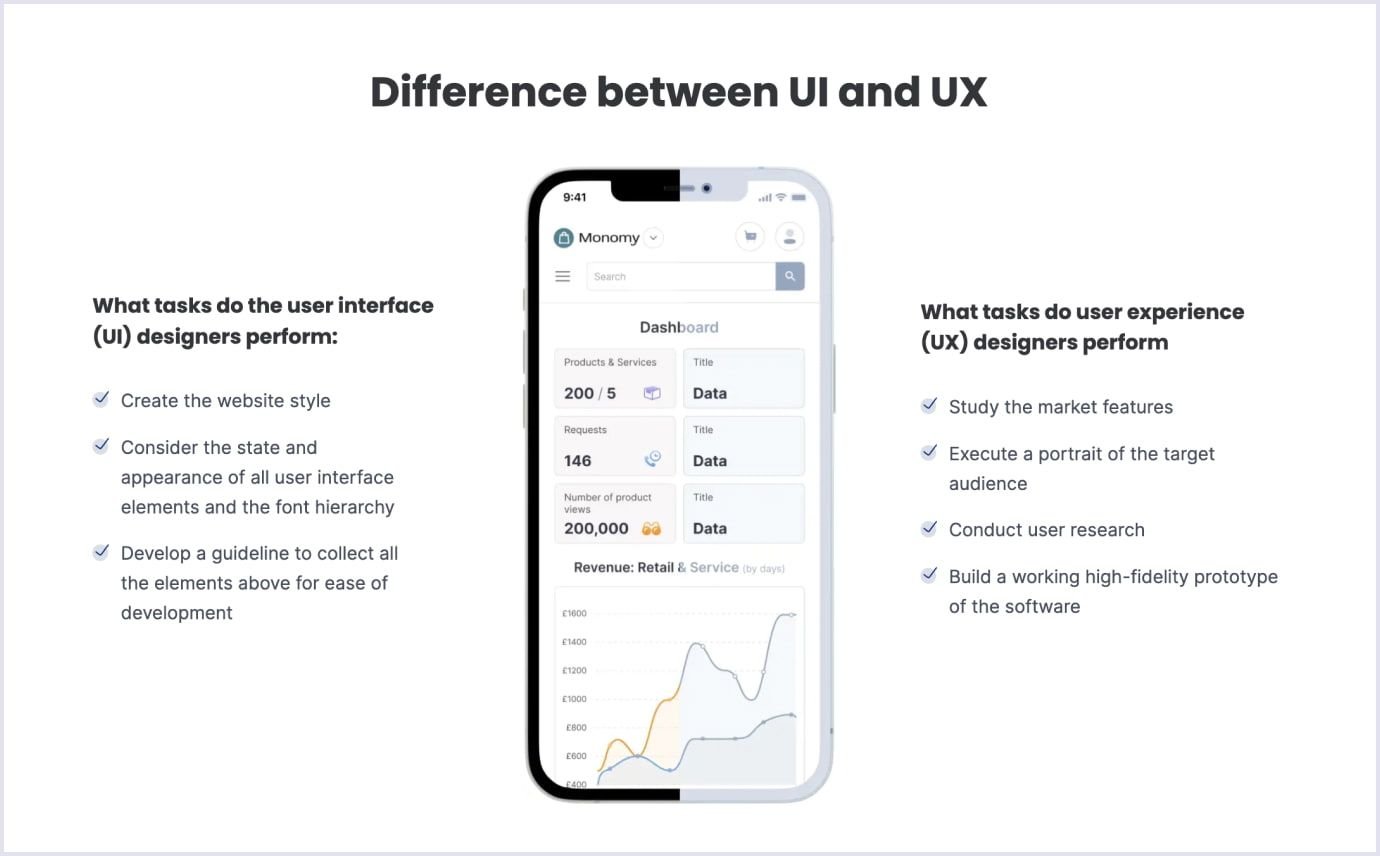
A well-designed UI/UX can have a great impact on the user's journey and make the app easier to use. Thoughtful UX can also increase user engagement and ultimately drive success for the app. On the contrary, a weak emphasis on UI and UX can lead to customer churn and simple confusion.
At Codica, realizing the vastness and importance of this step, we divide it into five phases. Each of them has unique objectives and tasks. Plus, it allows us to manage time and resources to comply with deadlines.

Research
Being the very first phase of the entire process, our designers start their work with in-depth research on the future product. With a solid analysis and a strategy background, they study the subject area of the project.
Besides, during the research, we pay enormous attention to not only the app itself but also how it will resonate in the market. Hence, it’s important to make it follow the latest UI/UX design trends.
The research phase is all about finding the right balance between functionality and user preferences. Hence, we refer back to the product discovery to see who are our potential competitors, what our future users will like, and how we can attract them.
Prototypes
In UI/UX design, prototyping is the process of creating a preliminary version or model of a mobile application.
It allows designers to test and refine their ideas and concepts before investing time and resources into the final product.
A prototype typically includes the basic layout, structure, and functionality of the product.
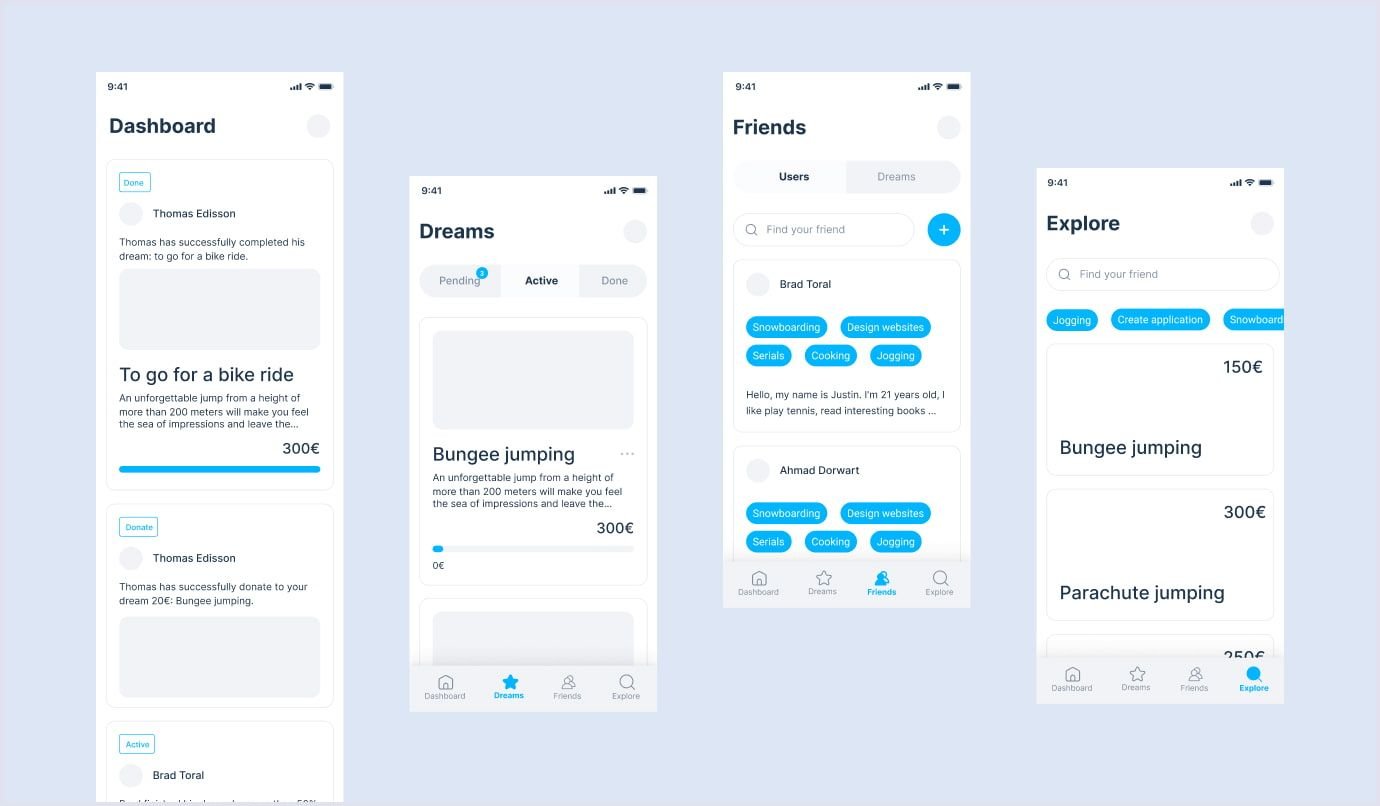
Prototyping helps designers to validate their assumptions, gather feedback from users, and identify potential usability issues before the product is built. It also enables clients to visualize and experience the product.
Visualization
Once we have finished with prototypes and they are approved – visualization comes into play. At this point, our design team conducts deep research on suitable color palettes, fonts, and other visual aspects of the future app. They are crucial to ensure the brand’s uniqueness.
In other words, during the visualization process, the designers’ mission is to ensure the style of the app is as appealing as possible to attract people to use it. Normally, we create several complex options for our clients to choose from.
Related reading: How to Choose the Right Font for Your Website: Typography Advice by Codica
Design & style guides
Once the visualization process is finished, begins the very last point in the whole UI/UX design of the mobile app. During the app design stage, we summarize everything we achieved during previous stages and compose detailed documentation. It serves as a reference for the design team, developers, and stakeholders to ensure that the app is built according to the agreed-upon design specifications.
For example, the documentation always consists of the following:
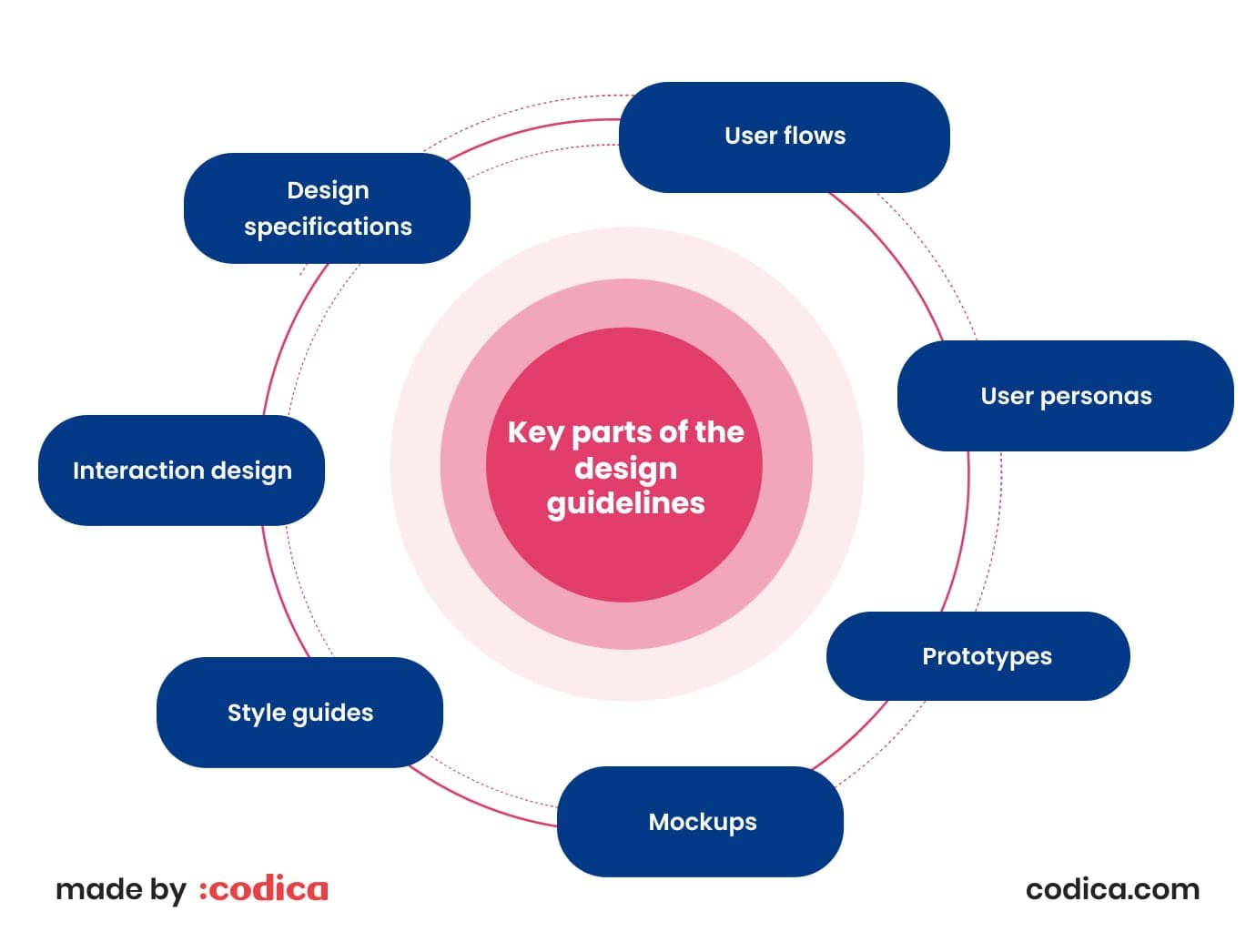
- User flows. They are usually presented in the form of a diagram or flowchart. It visualizes how users interact with the app. How they navigate through the interface, and which features they use. It maps the user's journey and allows the design team to optimize the usage, making it comfortable and more user-oriented.
- User personas. They stand for fictionalized characters that represent your target audience. Normally, the documentation on user personas includes complex researched data on users. Their demographics, goals, needs, and problems your app has to be able to help them solve.
- Prototypes. As mentioned before, prototypes are an essential part of the whole process. They can be very helpful for developers to get into the layout and functionality of each screen or page of the app.
- Mockups. Being a direct heir of the prototypes, mockups are a high-fidelity representation of the app. The main difference is that they already must include color schemes approved for the project, typography, and imagery.
- Style guides. Guidelines for the app's visual design. They include typography, colors, assets, etc. For example, designers have to provide maximum information about the typography and colors with their respective HEX/RGB codes and other details.
- Interaction design. This part usually includes details on how the app should respond to user actions. It includes animations, transitions, delays, and other interactive elements.
- Design specifications. They include instructions for developers on how to implement the design. Specifications consist of measurements, dimensions, and technical requirements.
Step 4: Active development phase
It's essential to define the technical architecture, pick a suitable technology stack, and define the development milestones before the app development process begins. However, the lion’s share of these things has already been defined during the project discovery. Consequently, adhering to our approach allows developers to provide mobile app development service without delays, as they have everything prepared.
Speaking of the actual development, though, there are various aspects on the way.
However, it is clear that the whole process of app development can be divided into two parts: a backend and a frontend. Let’s draw a line between them, shall we?
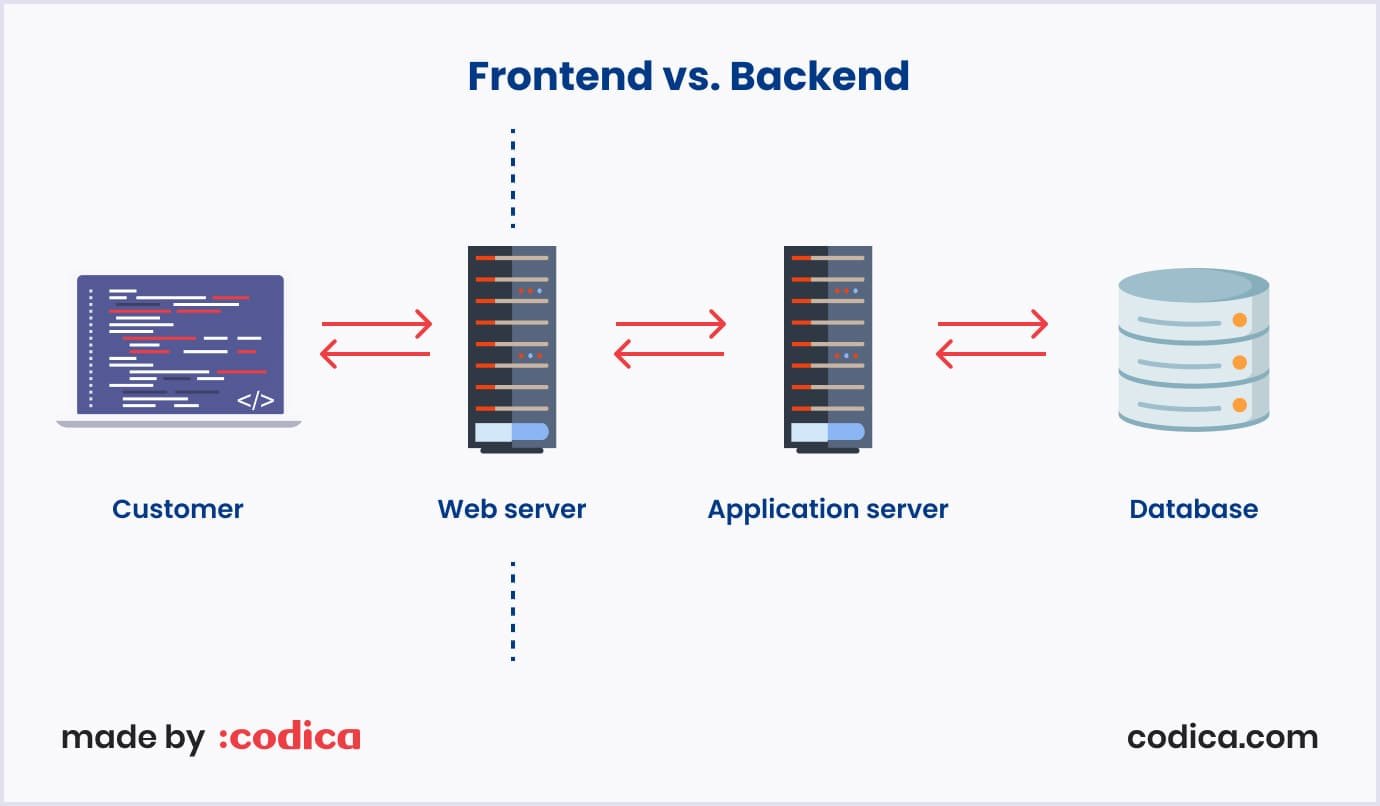
Backend
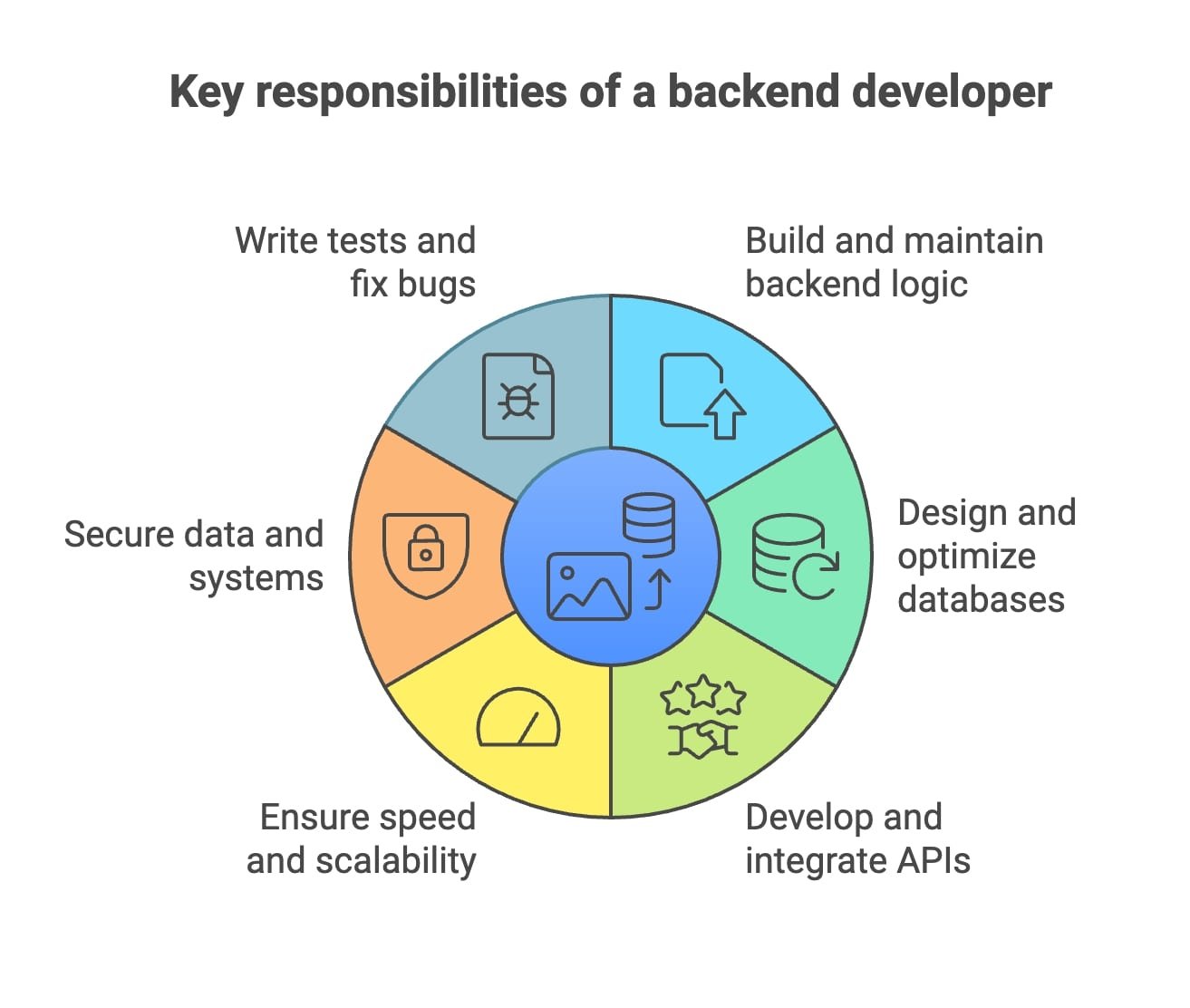
A backend part of the mobile application development process refers to the server side. It handles data storage, processing, and management. In simpler terms. It’s responsible for tasks like user authentication, data retrieval and storage, push notifications, and many more.
The backend mainly works with a database, a server, and an application programming interface (API). The latter connects the server and database to the mobile app. The server handles requests from the mobile app, processes them, and returns the required information to the user.
The database is responsible for storing and retrieving data. The API presents a middle ground between the server and the app. It makes their communication possible.
Mobile app developers use various programming languages and technologies to build the backend of an application, including Node.js, Ruby on Rails, PHP, and Python, among others.
Additionally, developers oftentimes rely on pre-built infrastructure and services to deploy and manage the backend of their mobile applications. Some such cloud-based services are Google Cloud, Amazon Web Services (AWS), and Microsoft Azure.
Frontend
In mobile app development, the frontend refers to coding the user interface and following the guidelines composed by designers. It is part of the app that users interact with directly, including the menus, buttons, screens, and animations. Nonetheless, it’s much more complex than simply building the UI of the app. Here are the essential parts it involves:
- Building the layout of the app. This involves creating the app's screens according to the documentation provided by the design team. Basically, the app has to be literally replicated from the guidelines, which makes it a very responsible task.
- Building the UI components. This step includes creating individual UI components such as buttons, text fields, checkboxes, search bars, and other elements. Besides, developers also have to import assets, fonts, and imagery to their working environment.
- Developing the navigation flow. This involves creating the logic that enables users to navigate through the app. It sets up menus, tabs, and buttons to manage transitions between screens and other functional parts of the application.
- Implementing animations and other visual effects. Based on the design team's perspective, developers have to replicate animations, custom transitions, and effects from the documentation. They make the app feel more engaging and intuitive for users.
- Integrating with APIs and backend systems. Frontend developers may need to integrate the app with APIs and other backend systems to access data on the web or cloud. They are needed to perform various tasks that require an internet connection.
- Testing and code reviews. When working on complex projects, it’s always worth the effort to test the app on various devices and platforms. Developers always identify and fix any bugs or issues that arise during the development process.

Step 5: Mobile application testing
It is a critical process in the development of any mobile application. Quality assurance services verify that the application is operational, user-friendly, and satisfies the intended requirements and specifications. In today's mobile-first world, apps have become irreplaceable in our daily lives. Consequently, it's important to ensure that apps are thoroughly tested before release.
In this section, we'll explore the various aspects of mobile app testing. We’ll take a look at the types of testing, how they work, and why you need them beforehand. However, we’ll organize it in a neat question-answer form for your convenience.
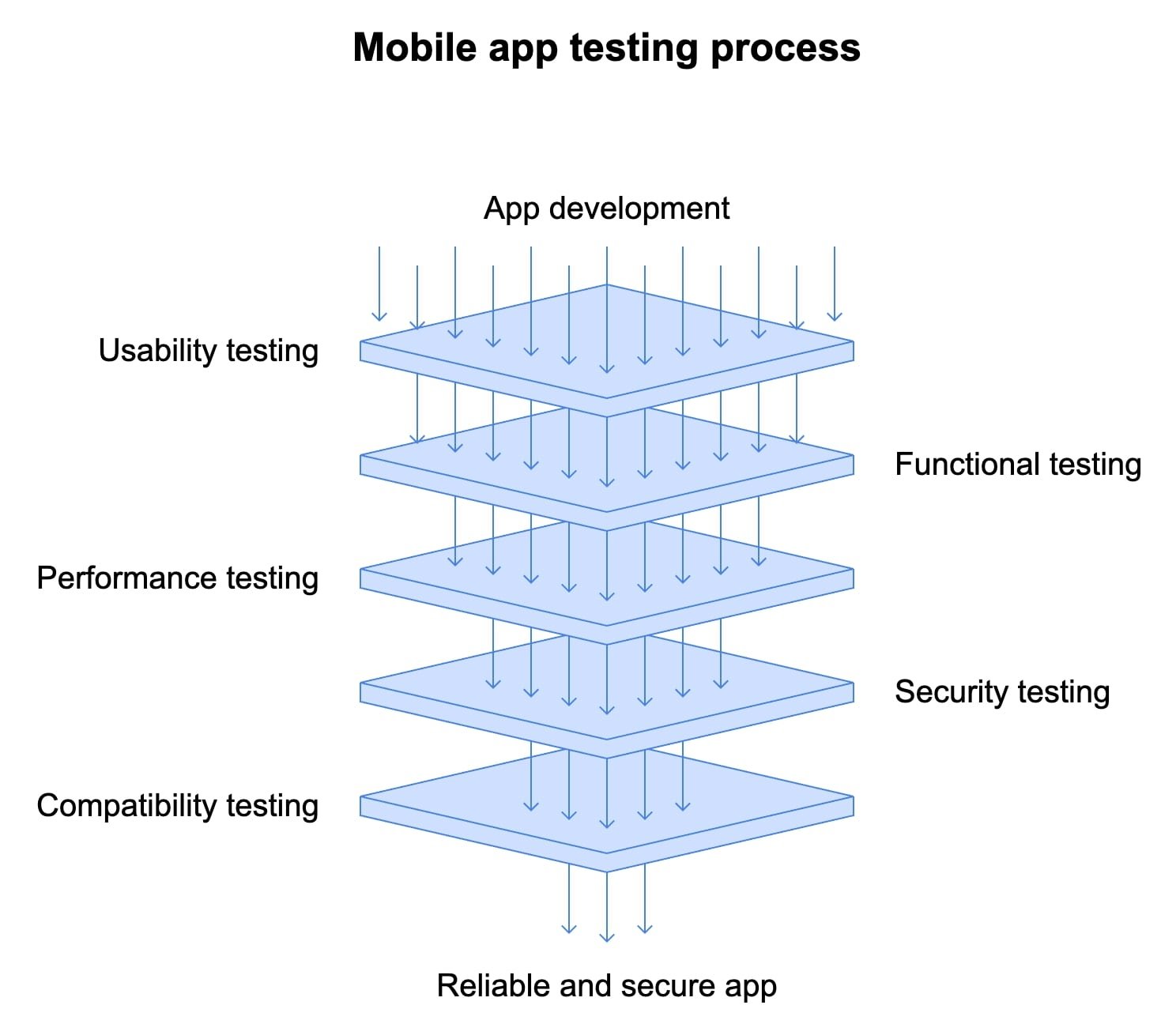
Usability testing
- What is it? Usability testing evaluates how easy and satisfying an app is for users, gathering feedback to identify issues and areas for improvement.
- When is it used? This testing can occur during the design phase, after a prototype is created, or post-launch to assess existing products.
- How does it work? Users are provided with scenarios or tasks to perform while interacting with the application. Observations and feedback help identify usability issues, which lead to design improvements.
Functional testing
- What is it? Functional testing ensures that every function of the app performs as expected and serves the user's needs.
- When is it used? It can be done at any level of maturity, usually after unit and integration testing, and prior to user-acceptance testing.
- How does it work? Test cases based on functional requirements are designed and then executed to verify whether the software behaves exactly as expected with both manual and automated testing methods.
Performance testing
- What is it? It is a testing that ensures an app can sustain levels of traffic in different states.
- When is it used? This testing can be done at any stage of the development life cycle, normally after functional testing.
- How does it work? Test scenarios emulate real-world conditions to measure responsiveness, stability, and speed, pinpointing bottlenecks and performance issues.
Security testing
- What is it? Security testing is a process aimed at checking for vulnerabilities and threats within an app to make it safe from unauthorized access and data breaches.
- When is it used? It is performed whenever new features are added and usually after functional testing.
- How does it work? The app is put to test against the set security standards through vulnerability scanning, penetration testing, and risk assessments.
Compatibility testing
- What is it? Compatibility testing is done to check on how the app performs over various hardware, software and network configurations.
- When is it used? Testing is done throughout the development cycle, generally after functional testing has been performed.
- How does it work? The application is tested on various devices and configurations to find out if there are any compatibility issues, hence ensuring that it works consistently across platforms.
You may also like: How Automation Testing Increases Execution Speed, Test Coverage, and Effectiveness
Step 6: Deployment
Once the app is planned, designed, built, tested, and polished to perfection – it’s about time to deploy it.
However, the deployment step is vast, to say the least. It differs for both Android, with Google Play Store, and iOS, with Apple’s App Store accordingly. Let’s reveal the peculiarities of app store optimization for both platforms.
App Store
The App Store is an online marketplace made by Apple Inc. It serves as the main platform for obtaining apps for Mac, iPad, and iPhone users. Here are the most controversial things about App Store you should consider.
- Submission and approval process. The App Store is known for its strict submission process. Normally, it takes around 2-3 days to receive approval and get the app published. However, apps can be rejected due to many reasons. The most common are security breaches, poor performance, and compatibility issues. Apple has a special team that carefully reviews each app and ensures that they publish only trustworthy and verified ones.
- Cost. Submitting your app to the App Store is pricey as well. A special Apple Developer Program, which works in the form of an annual subscription and costs $99. For the price, it enables you to submit apps and a handy set of tools for developers. For instance, devs can access cohesive analytical dashboards, the latest beta versions of the new software, and TestFlight. The latter is the app that allows developers to share their product in a test mode with up to 10,000 users to gather feedback.
Play Store
The Play Store is an Android app store that lets users browse and download numerous applications, games, books, movies, and other digital content. It is owned and operated by Google and is typically pre-installed on the majority of Android devices. It covers the broadest range of different devices with the only condition – support an Android OS. Here are aspects to think about before building an app for this platform.
- Submission and approval process. The Play Store has an efficient submission process, which generally gets the apps approved within hours or a couple of days. Such efficiency enables developers to release their apps as soon as possible and hence maximize their market opportunities. Google also provides detailed guidelines to comply with, which helps the developers understand what exactly is needed for approval and thus reduces the likelihood of rejection.
- Cost. Publishing on the Play Store is much more economical, with a registration fee of $25 for creating a Google Play Developer account. Such affordability makes it possible for startups, small-scale, and individual developers to present their apps to end-users. While other platforms require an annual subscription, this one time payment gives developers the ability to publish multiple apps without continuous expenditure and drives innovation and competition in the app ecosystem.
While advertising is an important source of revenue for many app developers, excessive ads can detract from the user experience and ultimately discourage users from continuing to use the app. Some users may feel that the frequency of ads is too high or that the ads themselves are intrusive or irrelevant to their interests.

Comparison
Obviously, both the App Store and Play Store have their nuances. They might seem frustrating, but it’s still important to know about them. Now, let’s look at a comparison table, which may be helpful in making a moderate choice.
| Aspect | App Store | Play Store |
| Application approval process | Strict and lengthy | Relatively faster and simpler |
| Application distribution | Exclusive for Apple devices | Wide range of devices from various vendors |
| Market share | Lesser. iOS owns a 28.37% market share in the mobile app world | Highest – 71% market share worldwide |
| Apps revenue share | Apple takes 30% of the share, leaving developers with 70% | Google also takes a 30% share |
| Allowed payment methods | Apple Pay | Google Pay and other payment services |
| User demographics | Tends to have a higher income and more loyal users base | The extremely diverse user base |
Step 7: Support and performance monitoring
After a mobile app has been released, the role of support and performance monitoring becomes crucial. This process makes sure the app expands and grows as expected. For more understanding, let’s divide support and performance into two different aspects and take a closer look at each. Here’s what you need to know about post-release support.
Support
- Addressing user issues. Once the app is published, the team becomes responsible for handling user complaints, feedback, and inquiries. They must respond promptly, courteously, and efficiently to resolve any issues and ensure a positive user experience.
- Bug fixing. When users report bugs or issues with the app, the team should take them seriously. They investigate, diagnose, and fix the problem as quickly as possible so it doesn’t affect users for a long time.
- Updates and maintenance. The team should ensure that the app is regularly updated with new content or features. Moreover, it has to be maintained to address any issues and provide new improvements.
Application performance monitoring (APM)
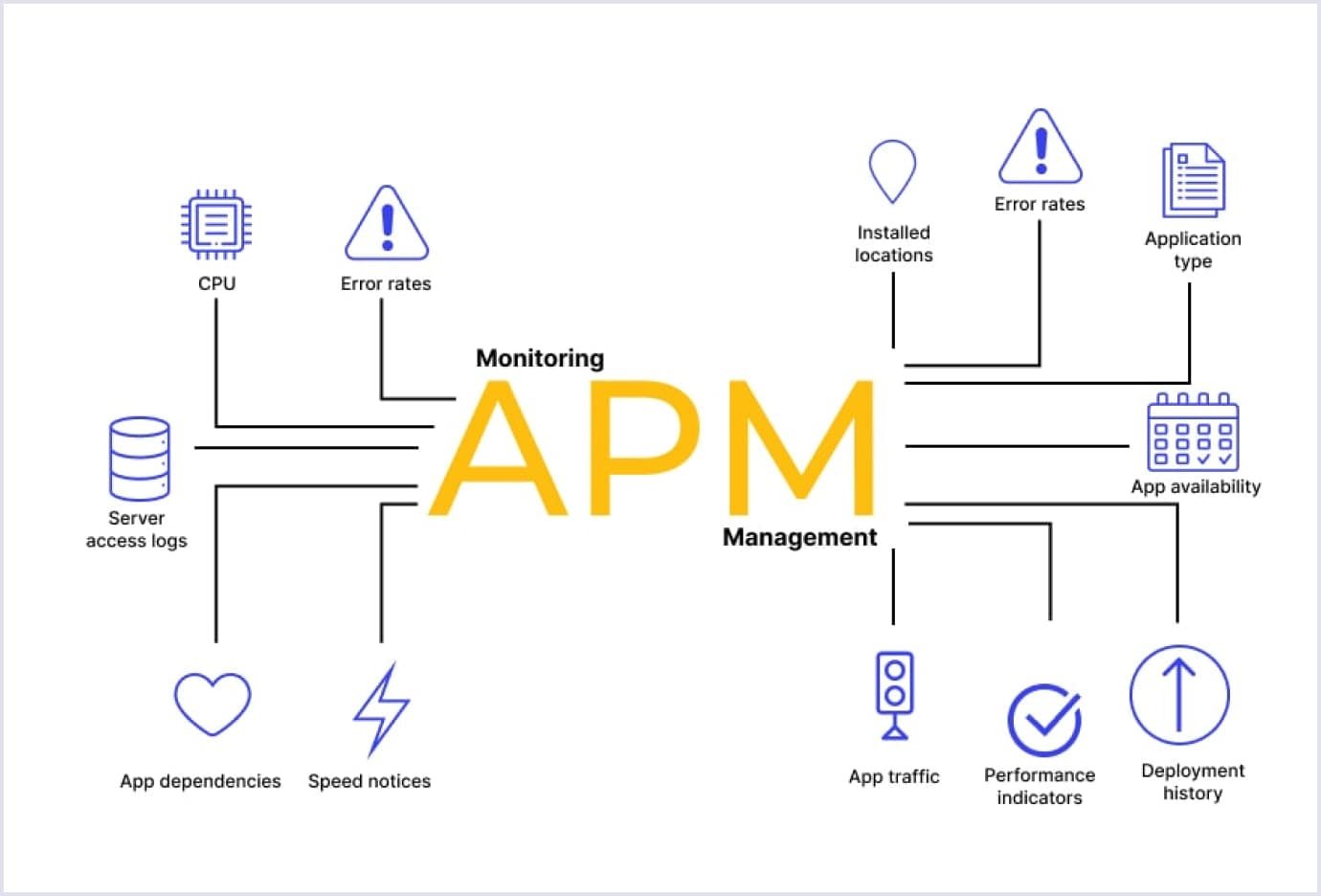
Source: Wallarm
- Monitoring app performance. This monitoring type involves regular key metrics tracking. They are user engagement, app crashes, load times, and server response times.
- Identifying performance issues. By monitoring performance, the team can quickly identify any issues that negatively affect the user experience. Then, they take steps to fix them.
- Optimizing performance. Monitoring can also help the team identify opportunities to optimize app performance. Some practices are reducing load times or streamlining user flows. The team should ensure that the app's infrastructure, servers, and databases are maintained and updated to ensure optimal performance.
Benefits of creating the app for your business
As the world shifts to a digital realm, businesses realize the importance of having a mobile app. In addition to providing customers with convenient access to their products and services, mobile apps offer a range of benefits for businesses of all sizes, which we will review next on.
Increase customer engagement
There are lots of ways that creating a mobile app can really help you to engage with your customers. A modern, well-designed app can do the following:
- Improve accessibility. It gives customers convenient access to your products and services. It is also extremely useful for users with special needs, as you can make the app very adaptable to ever-changing needs.
- Personalized users’ experience. If you create an app, you can collect data on what your customers like and what they do. This lets you make your business more personal for them. By offering them what they need, you can build stronger connections and get them more interested in what you do.
- Provide push notifications. Mobile apps can use push notifications to give customers real-time updates, alerts, and promotions, which websites can't do. This helps you stay on your customers' radar and create a sense of urgency that can drive engagement.
- Take advantage of social integration. If you add social media sharing features to your mobile app, you can use social proof to get more engagement and attract new customers.

Gain a competitive advantage
Needless to say, the right treatment of steps for developing an app can significantly boost your business’s performance. Here are some key aspects the app provides to do so:
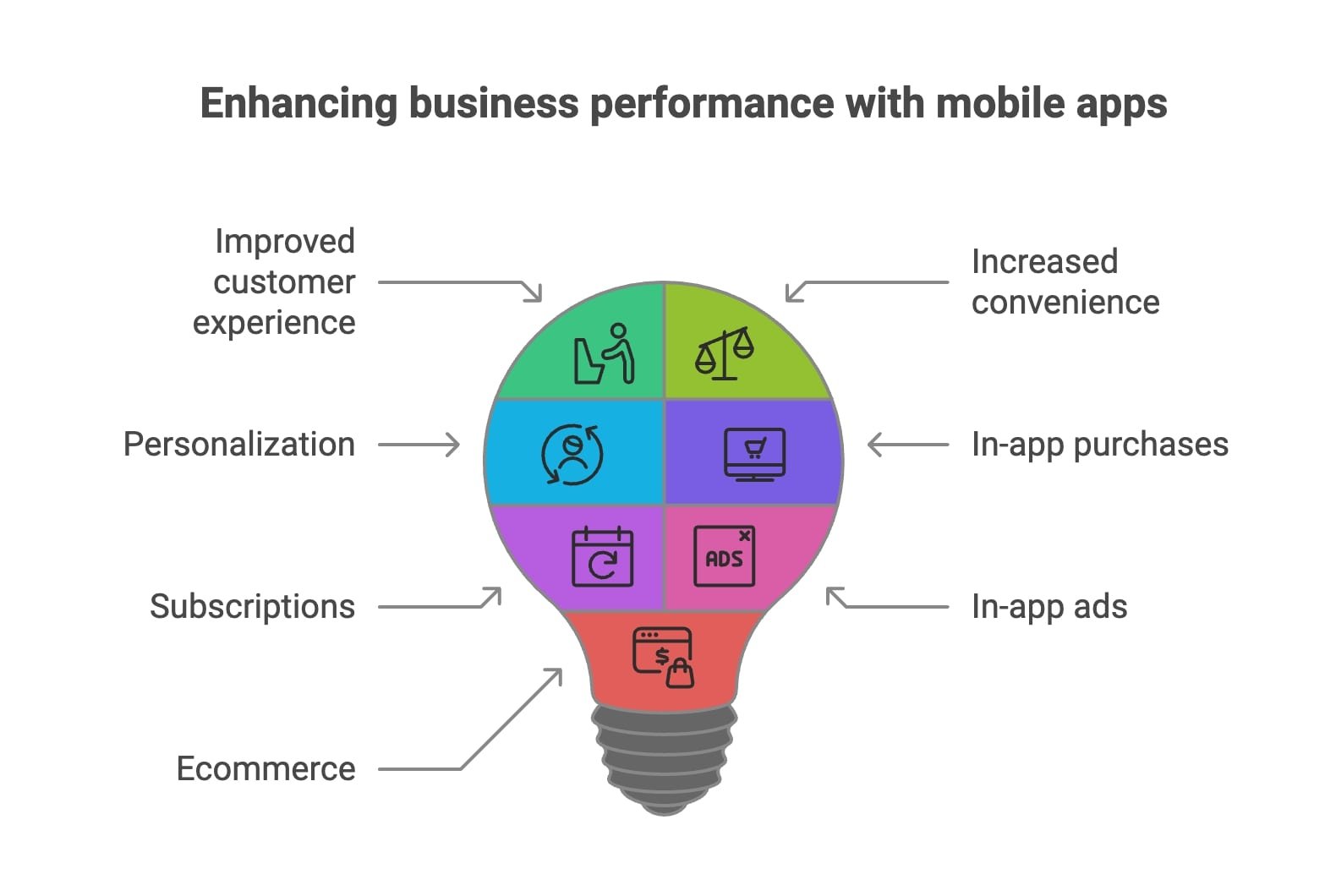
- Improved customer experience. A well-designed and user-friendly mobile app can enhance the customer experience. Thus, it will be easier for customers to engage with your business and increase loyalty.
- Increased convenience. Mobile apps give customers convenient access to your products and services. This can give your business an edge over competitors who do not offer a mobile app.
- Accent on personalization. A mobile app can provide customers with personalized experiences based on their preferences, behavior, and location. This can help you tailor your offering to their specific needs and differentiate yourself from the competition.
- Add in-app purchases. IAPs work quite simply. You can offer additional products or services within your application, such as premium content or features that customers can purchase for a fee.
- Add subscriptions. You can offer recurring subscription plans within your app. The most common options are monthly or annual subscriptions that provide access to exclusive content or features.
- Implement in-app ads. You can offer advertising space within your app to other businesses and generate revenue through advertising fees.
- Ecommerce. You can offer an ecommerce platform within your app, allowing customers to browse and purchase your products directly within the app.
Expanding your business with a mobile app is not just about reaching more customers. It is also an additional revenue stream that can either supplement or even equal your regular revenue stream. Here are some tips on how to gain additional income from the app:
How long does it take to build an app
First, arguably, the time for creating an app is highly volatile and depends on numerous factors. Accordingly, we’ll limit timeframes to months to neither disappoint nor encourage you. With that in mind, here’s a table outlining the general time frame needed to create an app.
| App type | Timeframe |
| Progressive web app (PWA) | 1-3 months |
| Simple app | 2-4 months |
| Hybrid app | 2-4 months |
| Cross-platform app | 4-8 months |
| Complex app | 6-12 months |
| Gaming app | 8-10 months |
It would be wise to turn to the pricing section next to shed more light on why the timeframe for each app type differs. Each app has a varying set of functionality, which, in turn, requires time to implement.
Mobile app development cost
Knowing that modern mobile apps are extremely diverse, it would be challenging to predict the price of a full-scale application.
Simply put, there are lots of aspects that influence the cost, and each app has a unique set of those aspects.
Accordingly, let’s follow another article of ours about mobile app development costs and overview them in smaller milestones.
| Aspect | Minimum price | Maximum price |
| Product discovery | $1000 | $15,000+ |
| UI/UX design | $5000 | $20,000+ |
| Development | $20,000 | $50,000+ |
| Testing | $5000 | $10,000+ |
| Support | $5000 | $10,000+ |
| Total | $36,000 | $105,000+ |
Conclusion
In conclusion, developing a mobile app can greatly increase customer engagement, improve employee experience, gain a competitive advantage, and even generate new revenue streams for your business.
But making apps can be difficult and time-consuming. A step-by-step guide like this one will help you develop your app smoothly and efficiently. Each step is important for making a successful mobile app, from planning to testing and launching. Focus on the user experience and gather feedback to improve your app.
Codica is a dedicated, hard-working, and attentive-to-detail partner for your mobile app development needs. Feel free to review our portfolio, and contact us to develop a high-quality mobile app that meets your users' needs and drives growth for your business.
