Cloud computing services have long been a standard practice for businesses. More and more companies harness the power of the software as a service (SaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), and infrastructure as a service (IaaS) models. Thus, it is crucial to understand their differences when planning to build a SaaS product.
In this article, we discuss the IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS models and define their principal differences. Hence, let’s start with the definition.
What is cloud computing?
Basically, cloud computing means that on-demand computing services are delivered over the Internet on a pay-as-you-go basis. This model allows storing and accessing data and apps in remote data centers, so you no longer need to keep them on your hardware.
Today, more and more companies are switching from on-premise technologies to cloud development services. This trend has led to the growth of the global cloud computing market. For example, Gartner's forecast for SaaS vs. PaaS vs. IaaS revenue looks favorable: $917 billion by 2025.
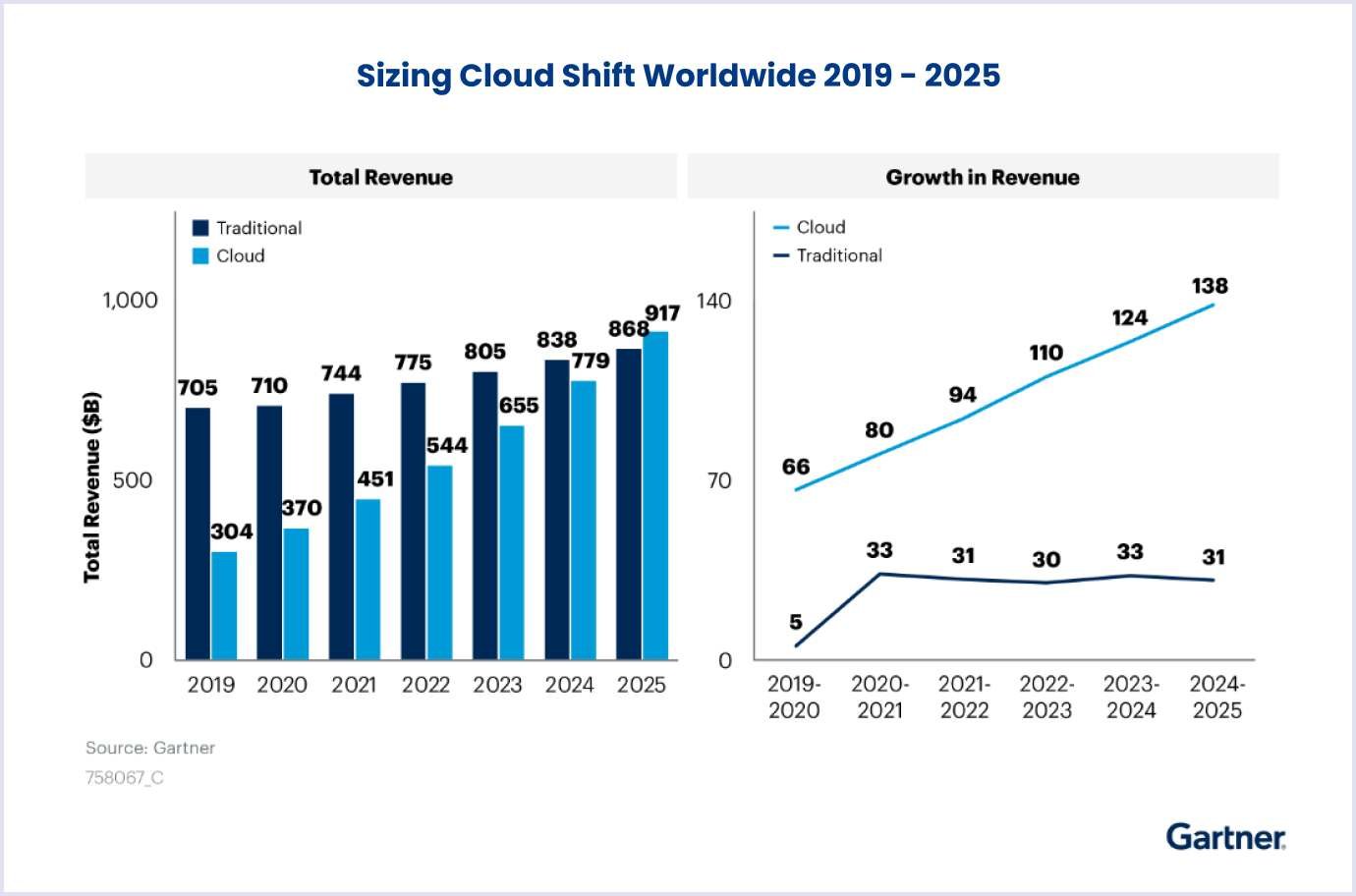
It looks promising, doesn’t it? So, let’s look even closer. There are three main models among many cloud computing approaches: IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS. Here’s everything you should about each.
What is IaaS?
Infrastructure-as-a-service refers to self-service that enables users to access and monitor hardware. This cloud computing model includes monitoring of specialized processors, data storage space, and visualization services. It is like using a physical data center.
The main characteristics of IaaS cloud service include the following:
- The service provides development resources;
- You pay as much as you use;
- Services are scaled easily;
- One piece of hardware is available for many users;
- IaaS providers have complete control over the computing infrastructure;
- Ensures dynamics and flexibility for developers.
When to use IaaS
Let’s discuss cases when IaaS seems the best possible option if you have to choose between IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS:
- Your startup lacks the funds required to create your infrastructure.
- You work with big data. In this case, infrastructure-as-a-service is what you need. It is noted for its ability to cope with large workloads. Besides, this cloud computing service is compatible with business intelligence tools. With their help, you can predict industry trends and create innovative products and services.
- Your company is experiencing rapid growth. With IaaS solutions, you can easily change particular hardware or software according to your evolving needs.
- You do not have precise requirements for your application. IaaS is noted for its flexibility and scalability.
Benefits of IaaS cloud model
- On-demand scalability. A clear benefit of the IaaS cloud model is that it can be scaled fast according to your company's growing business requirements. IaaS vendors offer the most powerful storage and networking technology to satisfy their customers' needs.
- Great reliability. Suppose a certain hardware component fails or you lose an Internet connection. These technical issues will not affect your infrastructure. Besides, IaaS vendors spread the system’s workload across multiple data centers and servers. Thus, computing resources, hardware, and cloud-based apps will always be available.
- Operational flexibility. IaaS enables your team to access the hardware, computing power, and applications used regularly. As a result, they can view the required files and data on the go anytime.
- Disaster recovery (DR) and business continuity (BC). Most DR plans are expensive and bulky. A company needs to set separate DR and BC plans for each branch if it has several branches. Meanwhile, IaaS combines DR and BC in their service plans. If a disaster occurs, a company can rely on them, reducing costs and saving business manageability.
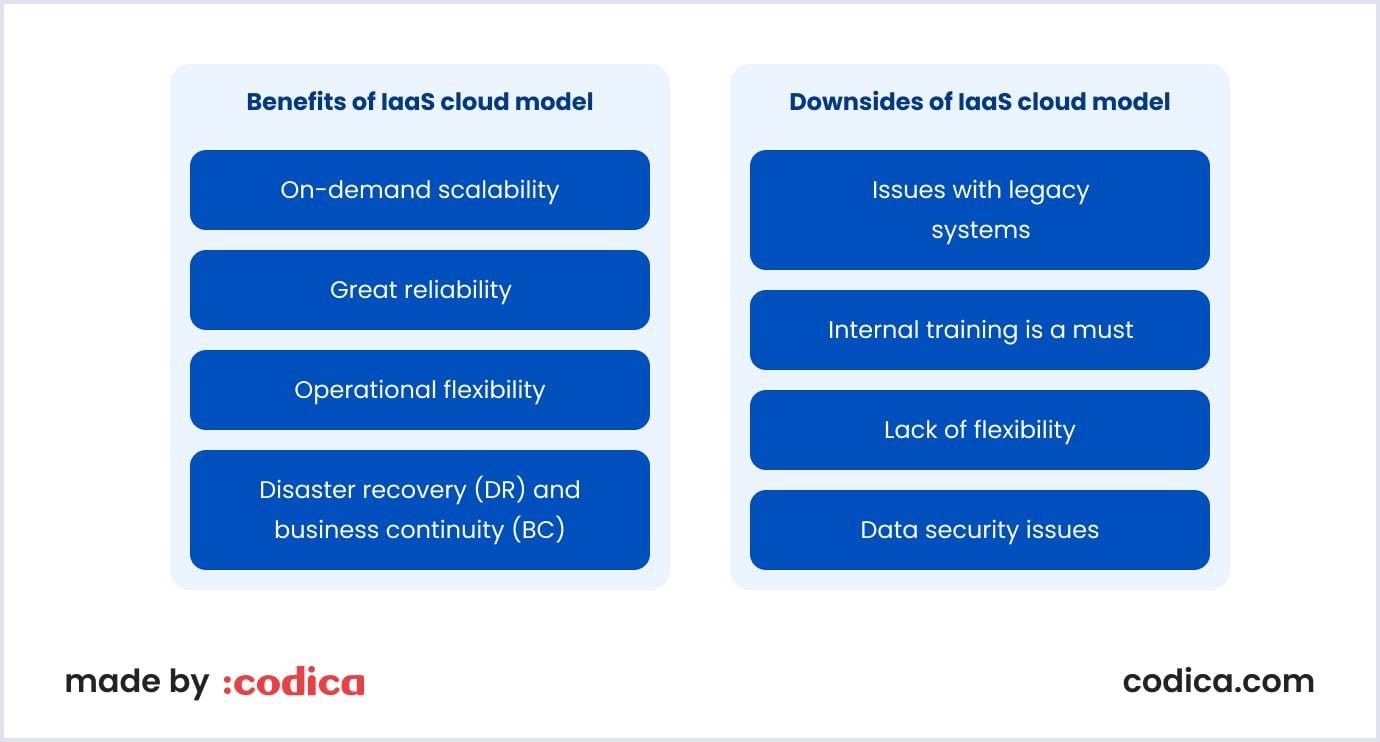
Downsides of infrastructure-as-a-service
- Issues with legacy systems. It is possible to run legacy applications in the cloud. However, the infrastructure may not be designed to secure such apps. This fact forces you to enhance your applications before you move them to the cloud.
- Internal training is a must. With IaaS solutions, you will deal with data security, backups, and business continuity. It means that your team will have to learn how to manage new infrastructure. Otherwise, the process of monitoring and managing resources can become too complicated.
- Lack of flexibility. IaaS vendors maintain and upgrade both hardware and cloud-based software. If services that you work with are not updated regularly, the efficiency and productivity of your team can be compromised.
- Data security issues. IaaS lets you control apps, data, middleware, and the platform OS. However, you cannot monitor the security of communication between the infrastructure and virtual machines. Thus, you depend on the security measures that your IaaS provider offers.
Examples of IaaS
The prominent IaaS solutions are as follows:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS). It is an agile and secure cloud computing platform. Global banks and military organizations entrust AWS to handle their data.
- Google Compute Engine (GCE). With this compute engine, you can create virtual machines and run them in Google’s infrastructure.
- Digital Ocean. This IaaS is known for its low prices and scalability. Digital Ocean infrastructure allows users to start working in the cloud quickly.
- Cisco Metacloud. It is an agile, robust, and scalable environment for building private clouds.
Below is how AWS offers to explore their analytical, computing, and other products:
Read also: Top SaaS Startups for Your Inspiration in 2024
What is PaaS?
PaaS refers to platform-as-a-service and provides users with a cloud environment for creating custom apps. This is different from SaaS, which offers ready products. With PaaS cloud service, you do not have to build and maintain the infrastructure required for your application.
The main characteristics of PaaS include the following:
- Based on virtualization technology. So, you can scale PaaS resources as your business changes;
- Offers services to develop, test, and deploy solutions;
- Can be accessed via the same development environment;
- Includes operating systems, databases, and web services.
When to use PaaS
When you have to choose between SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS, opt for platform-as-a-service solutions if:
- You are engaged in custom software development services.
- Several developers in your company are working on the same project. In this case, platform-as-a-service products add flexibility and speed to the whole process.
- Your company develops mobile applications. With PaaS flexible solutions, you can build cross-platform applications. They will be adapted for any device and operating system.
Benefits of PaaS
- Cost-effectiveness. With PaaS cloud-based solutions, you no longer need to build applications from scratch. So, it is a good option if you have limited resources or want to reduce your operating costs.
- Quick launch. Prebuilt backend infrastructure allows rapid prototyping and development. As a result, you can release your application in no time. The early launch, in its turn, increases your chances of success.
- Reduced development time. PaaS vendors give you access to various libraries, frameworks, templates, and other tools. All those instruments speed up and simplify the whole development process.
- Quick testing and deployment. PaaS allows for flexibility in access to different machines and configurations to test your app. This provides rich opportunities for testing the performance and compatibility of your apps so you can make changes to the apps made in PaaS in a shorter time.
- Easy maintenance. Platform-as-a-service frees developers from building, updating, and configuring servers, which are the responsibility of PaaS providers.
- Quick sharing of data in teams. PaaS products usually allow for the sharing of data among many development teams. Thus, a company does not need to allocate the same resources to separate development teams.
- Data integration and aggregation. Creating applications typically implies data integration and aggregation over time. PaaS systems include the necessary components to speed up development work.
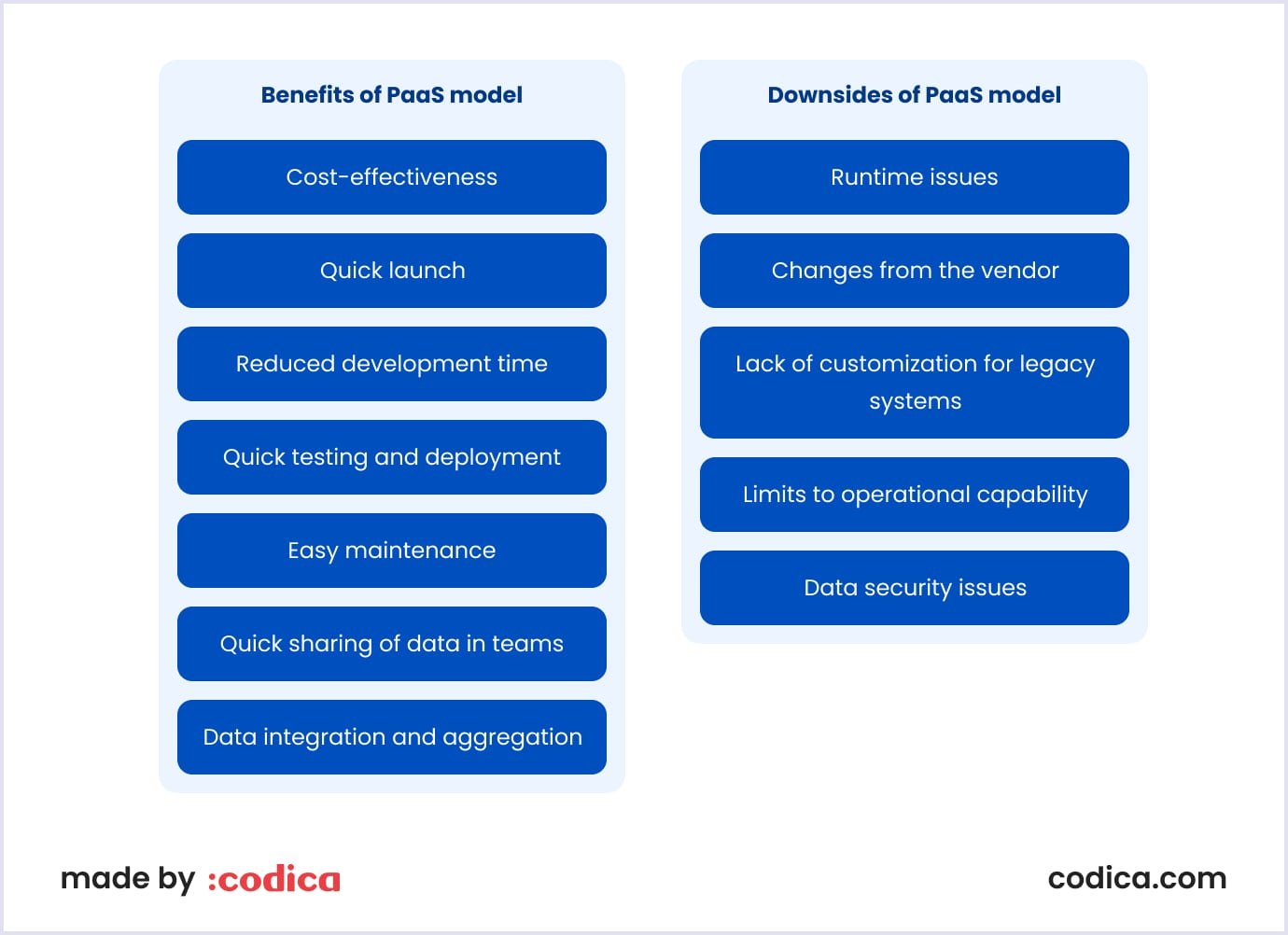
Downsides of the PaaS model
- Runtime issues. Sometimes, you may find out that PaaS service models are not customized for the programming languages and frameworks that you want to use. Also, it may happen that the particular version of a framework is not available with the PaaS cloud-based services.
- Changes from the vendor. Changes in the PaaS vendors' current architecture can become a severe issue for you. Let’s see how it works. Suppose you work with Ruby language. It is compatible with the cloud solution you use. Suddenly, the provider rolls out an update that requires Python for further compatibility. You have two options: changing the programming language or using the PaaS provider.
- Lack of customization for legacy systems. If you have legacy applications or services, you may notice that they do not function well with PaaS products. To address this issue, you will have to invest heavily in customization and configuration changes.
- Limits to operational capability. Customized cloud operations have automated workflow management, which might not work well with PaaS solutions. Thus, operational options may be limited for your end users.
- Data security issues. PaaS service models allow you to run your own solutions or services. However, you do not control the data hosted on cloud servers managed by third parties. Therefore, security depends on the PaaS provider and third parties. If your customers have certain hosting policies, they might not be able to deploy their services.
PaaS delivery
Basically, delivery of PaaS is the same as that of SaaS. The only difference is that PaaS does not deliver software over the web but offers the environment. PaaS relieves developers from worry about infrastructure, operating systems, or data storage.
Developers design and create software using special components built into PaaS. These components include operating systems, development tools, and middleware.

PaaS examples
- Microsoft Azure. This platform enables you to build, test, and host apps. Also, you can synchronize and integrate various virtual devices.
- Google App Engine. It requires that apps are built in Java or Python. Google App Engine provides developers with scalable hosting and top-notch Internet service.
- AWS Elastic Beanstalk. It is a cloud service that allows you to deploy and scale web apps and services. The platform is offered by Amazon Web Services.
- Red Hat OpenShift. With this service, you can build and deploy apps to one or many hosts. The platform allows you to use any programming language for this.
- Heroku. This PaaS allows you to create, manage, and scale modern web apps. It helps you build web applications that scale well with traffic spikes or high loads.
For an example of PaaS, Heroku offers this extensive feature set:
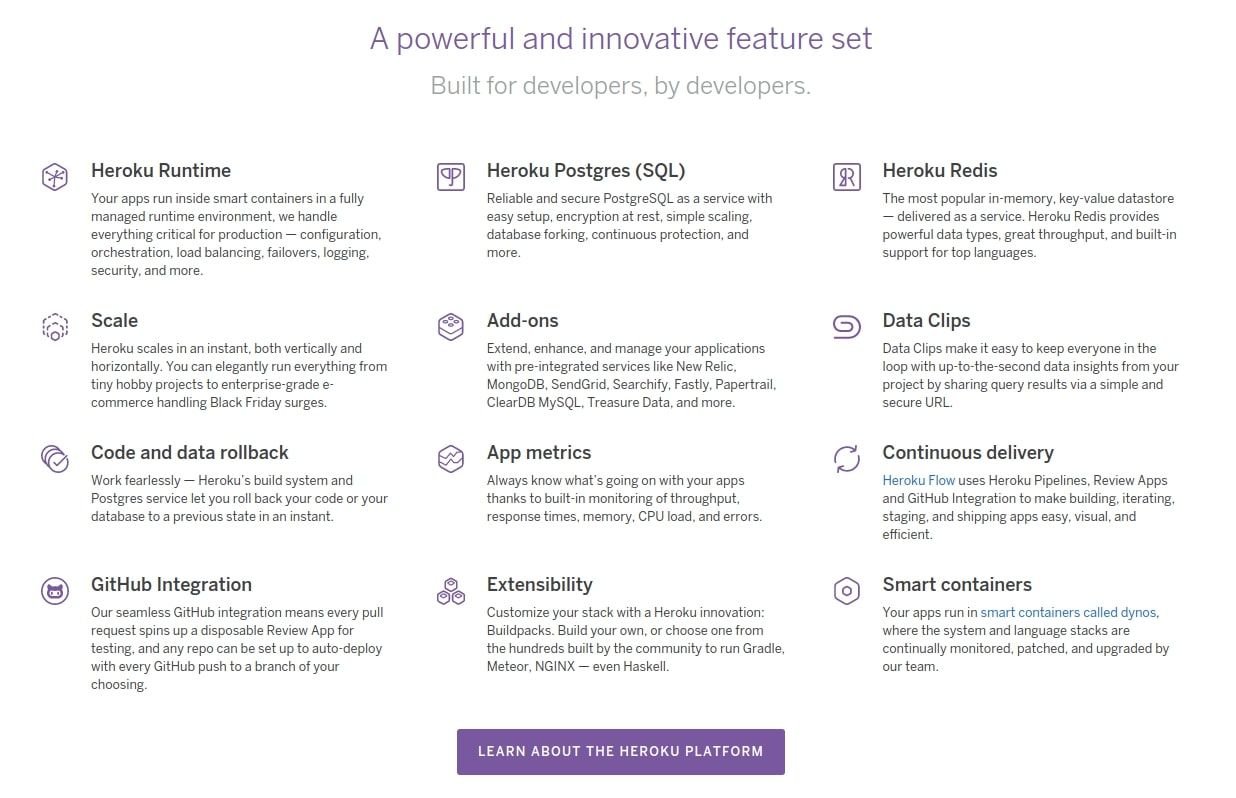
What is SaaS?
Essentially, SaaS means ready software products delivered via the Internet on a subscription basis. If we compare SaaS vs. PaaS vs. IaaS, the first cloud service model is the simplest option to maintain. The third-party provider fully manages SaaS by making updates and supporting software. That is why most businesses use it for their operations.
You only need a web browser to run a SaaS app. Unlike on-premises solutions, SaaS does not require installations or downloads. The main characteristics of SaaS apps include the following:
- Controlled from a central point by a third-party provider;
- Hosted on a remote server;
- The software can be accessed over the Internet;
- The provider is responsible for SaaS updates.
When to use SaaS
Software-as-a-service is the most suitable option among IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS in the following cases:
- Your startup needs to launch a project quickly. You have little time to deal with server issues.
- You will use the app from time to time, like tax software.
- You are working on a short-term project that requires fast collaboration.
- Your application needs both desktop and mobile access.
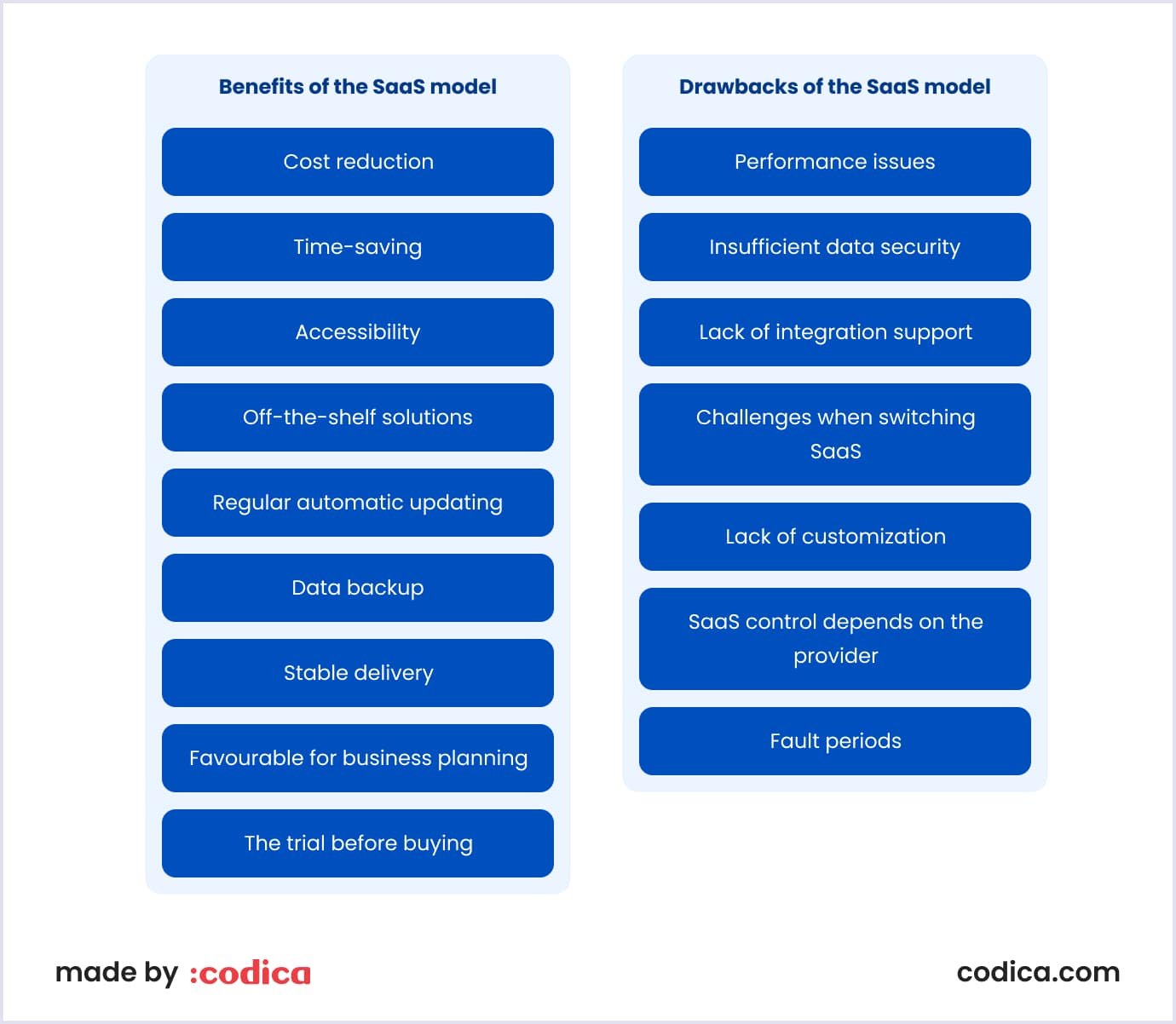
Benefits of the SaaS model
- Cost reduction. Regarding SaaS technology, vendors are responsible for handling potential technical issues. They deal with data, servers, and storage networking. They also provide their service users with maintenance, compliance, and security services, which can significantly cut expenses.
- Time-saving. Software products do not have to be downloaded and installed on individual devices, freeing the technical staff from tedious tasks related to installing or upgrading the software.
- Accessibility. SaaS applications are easily accessible. All you need to use them is a computer or a mobile device with a stable Internet connection. Thus, SaaS products are handy for teams working remotely.
- Off-the-shelf solutions. Software-as-a-service vendors offer out-of-the-box products that are easy to set up and use. Both basic packages and more complex solutions are available for you.
- Regular automatic updating. Providers include automatic updates in the SaaS solutions. Thus, their customers have no worries about updating the software.
- Data backup. SaaS includes backup software. It is a special technology that helps store and protect data created with a SaaS product. The technology is included in the SaaS and delivered via the cloud, so companies save on backup and storage of their data.
- Stable delivery. SaaS providers care about their customers’ best experience with the products. Thus, they ensure the stable work of their SaaS solutions as much as possible. This means that your business works with minimum downtime.
- Favorable for business planning. SaaS providers handle complex computing operations and their users' daily activities. You pass software installations, updates, and maintenance to a SaaS provider. So, you focus on running and developing your business.
- The trial before buying. It is a widespread practice for SaaS providers to offer a trial period for customers. So, you can test how an app works for your company before investing in the system introduction.
Drawbacks of the SaaS model
- Performance issues. Internet-dependent applications running on remote data centers sometimes may show poor performance. At the same time, apps installed on your employees’ computers may perform much better. To avoid this issue, you should invest in a reliable and fast Internet connection. Besides, you need application performance management tools to check the performance of the SaaS apps over time.
- Insufficient data security. This is one of the main reasons why some companies are hesitant to switch to the software-as-a-service cloud. Thus, access management becomes your priority. Consider this issue before entrusting a third-party service provider with your sensitive information.
- Lack of integration support. Some SaaS products need to be integrated with other tools and applications that your company uses. Thus, you will automate your business workflow and increase your staff’s productivity. In this regard, software-as-the-service vendors may provide you with limited support. As a result, you will have to invest internal resources to manage these integrations.
- Challenges when switching SaaS. This issue is called vendor lock-in. This means a user or a company depends on a vendor to use a product. Shifting to another vendor implies significant resources and time expenditures. In relation to SaaS, it means that it may be challenging to switch to another software cloud solution. In case of migrating to another SaaS, end users incur significant costs for changing or need in-house engineering rework.
- Lack of customization. On-premise software comes with different development kits (SDK). They allow you to tune up a solution as your business requires. Meanwhile, SaaS has low customization capability. Such software is designed to fit the most widespread needs. Thus, SaaS can lack custom features or will not meet performance requirements.
- SaaS control depends on the provider. You entrust the provider with control over a SaaS solution. First, such control includes updates of functionality and interface. What’s more, the provider also controls data security and governance models. This means that end users will need to adapt their security and governance models to the features included in SaaS.
- Fault periods. Since the provider manages SaaS, your customers depend on its proper work. Maintenance and dealing with cyberattacks and network faults lead to downtime. So, you and your customers must wait until the provider finishes planned and unplanned work.
SaaS delivery
Providers deliver SaaS solutions to end users via the Internet. Typically, you can use a SaaS solution as an app or install it on your device. For example, you can use Google Docs over the web. Meanwhile, you need to download Adobe Creative Cloud to your computer.
What is great about SaaS is that you don’t need help from IT specialists to install the app on each device. Providers manage software and hardware updates, saving your time and resources.

SaaS examples
- Dropbox. A cloud storage solution for storing and sharing files;
- Hubspot. A customer relationship management (CRM) and service SaaS platform that companies use to attract and retain customers;
- Jira. A team management software for issue tracking and project management;
- Salesforce. A CRM tool for support, sales, and marketing teams globally;
- Zendesk. A tool allowing you to manage interactions in customer support;
- Mailchimp. A SaaS platform helping to optimize email marketing processes;
- Slack. A messaging program for efficient teamwork;
- Google Workspace. A group of online workspace apps for streamlining business processes;
- Microsoft Office 365. A suite of productivity tools, an online version of traditional Microsoft Office apps.

IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS comparison
Now, you are familiar with three main types of cloud computing. These types define how you use the cloud for your enterprise, i.e., hosting, storing, managing, and processing data online.
To summarize, here's a table outlining the core differences between IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS.

Codica’s choice for cloud solutions
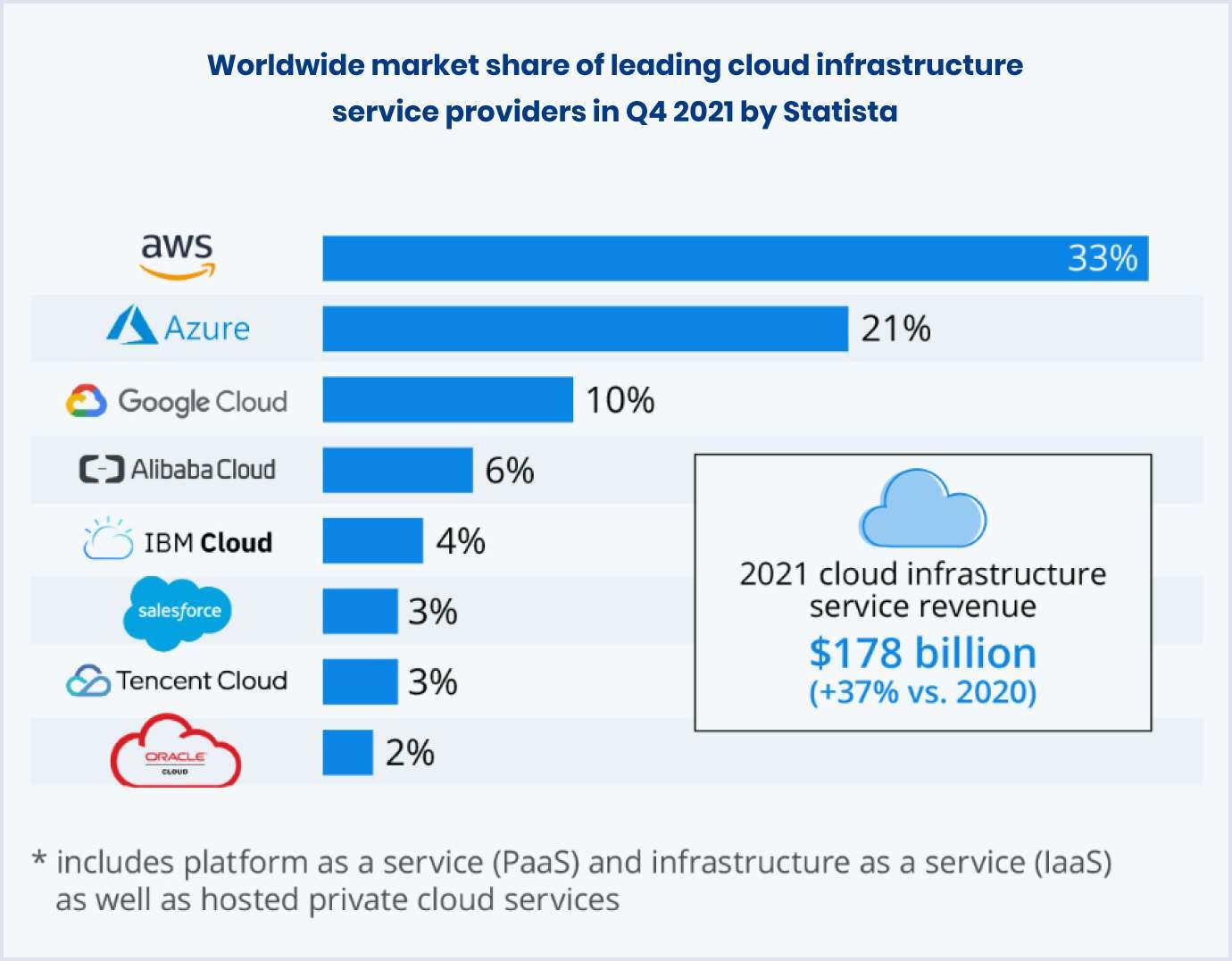
Regarding the advantages of cloud solutions, our team likes to use them in custom software product development. According to Synergy Research Group, the three major players in the cloud infrastructure market are Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud.
Here are our favorites.
AWS. This cloud platform allows developers to deliver apps that run seamlessly. Using this IaaS provider, developers can choose the operating systems, programming languages, and web app platforms that best suit a particular solution. Also, AWS ensures the security of the cloud. That is why we use AWS in our DevOps security practices.
Sentry. At Codica, we check our code to make it optimized and ensure that the app runs smoothly. That is why we use Sentry. This error-tracking SaaS tool helps us ensure that the code we created is bug-free and efficient. Thanks to this, a solution works fast and provides the best user experience.
Dropbox. It provides automatic file backup. This means that a user does not need to back up files on their hard drive, which saves users time and space when backing up files. Also, recovering files is simple and does not require special tech knowledge. Dropbox integrates well with other software systems, such as Microsoft and Slack. Furthermore, the tool allows you to make changes if you are offline.
HubSpot. This CRM is free to use and has reach functionality to track user behavior. The SaaS easily integrates with social media, which is why we recommend our clients include this tool in their solutions.
Further reading: How Much Does It Cost to Build a SaaS Product in 2024: Detailed Guide
Conclusion
We have discussed the main difference between IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS cloud models. As you can see, each company offers particular benefits. Knowing cloud services’ pros and cons, you can choose the best model for your business.
Do you have an idea for a cloud product in mind? Are you looking for reliable SaaS development services to take on the technical part? Contact us, and we will be happy to discuss your project idea. We have vast experience in building SaaS applications. We will eagerly provide you with a scalable and secure cloud solution

